AI Design Tools

Designers are always looking for the next big thing that will help them to simplify their workflow. It’s no wonder that AI has made its way into nearly every aspect of design from fashion to space exploration. Designers big and small are learning just how to get the most out of this powerful new tool.
Graphic Design
When most people think of “design” they typically think of logos, signs, and images. Here, AI has proven to be an incredibly powerful assistant.
Nutella, the famous chocolate and hazelnut spread brand, used an algorithm to generate seven million unique packaging designs for their jars. Working with the advertising agency Ogilvy & Mather Italia, Nutella created software that combined different patterns, colors, and brand logos in different arrangements to generate millions of unique designs, which were then printed and distributed worldwide. The designs were meant to appeal to younger consumers and encourage them to share their favorite designs on social media. The campaign was successful, with Nutella reporting an increase in brand engagement and sales. The use of AI in design allowed Nutella to create a vast number of unique designs that would have been impossible to create manually.
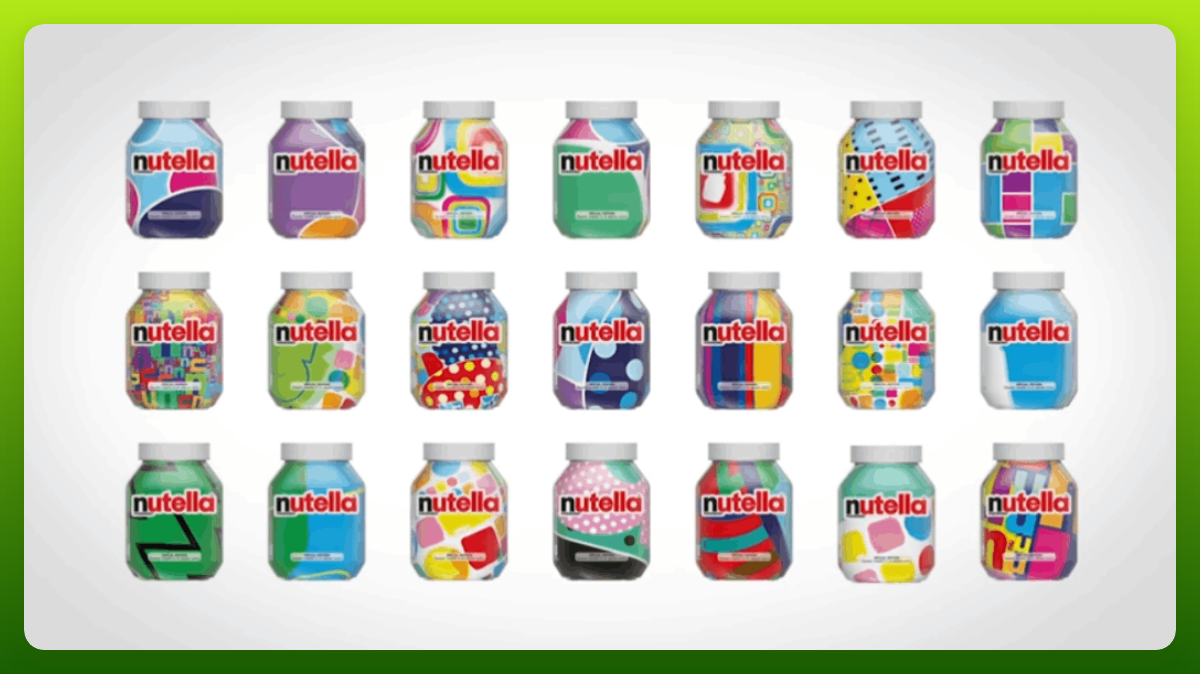

But it’s not just large-scale global brands that can make the most of AI. Smaller designers have also had a field day.
Finding the exact right image for your project is a tedious job at the best of times. If you can’t find exactly what you want in the right colors, resolution, or license-free you’ll either have to scrap the idea or make your own. For a lot of people, just designing an image isn’t a simple task. Luckily, this is an area where AI has been incredibly powerful.
Joy Zhang is a tech blogger who has been playing around with AI design for a bit and hither insights are incredibly helpful for newbie users.
Joy set out to create a very specific image; they wanted a llama playing basketball. A quick Google image search gives a few options, but nothing really captured exactly what Joy was looking for.
What’s an aspiring designer to do? Well, luckily, AI Image generator Dall-E was in public Beta at the time so Joy decided to check it out. They started simply and asked Dall-E to draw exactly what they wanted.
“A llama playing basketball”

Well, that is certainly a selection of images of a llama playing basketball. However, these aren’t exact;y “good”. I mean, they’re better than I could draw up, but Joy wanted something a bit more lifelike.
Why was Dall·E defaulting to cartoon images for this prompt? Most likely it has to do with e lack of actual images of a llama playing basketball seen during training. This highlights one of the biggest weaknesses of AI, it can’t go beyond what it’s already been told.
The next prompts were all about adding more detail.
“Realistic photo of llama playing basketball”

OK, now we’re getting somewhere. While these llamas are looking much more lifelike, the entire image looks like a bad Photoshop challenge. It’s clear that composition isn’t Dall-E’s strongest suit. This brings us back to what is becoming to biggest trend in any discussion of using AI: prompt generation.
Prompt engineering is basically the process of designing prompts to give you the desired results. The Dall·E 2 Prompt Book is a fantastic resource for this, with a detailed list of inspirations for prompts using keywords from photography and art.
AI tools are powerful, but they can’t read minds…yet. Until then, you need to be able to tell it exactly what you want.
“Film still of a llama dunking a basketball, low angle, extreme long shot, indoors, dramatic backlighting.”
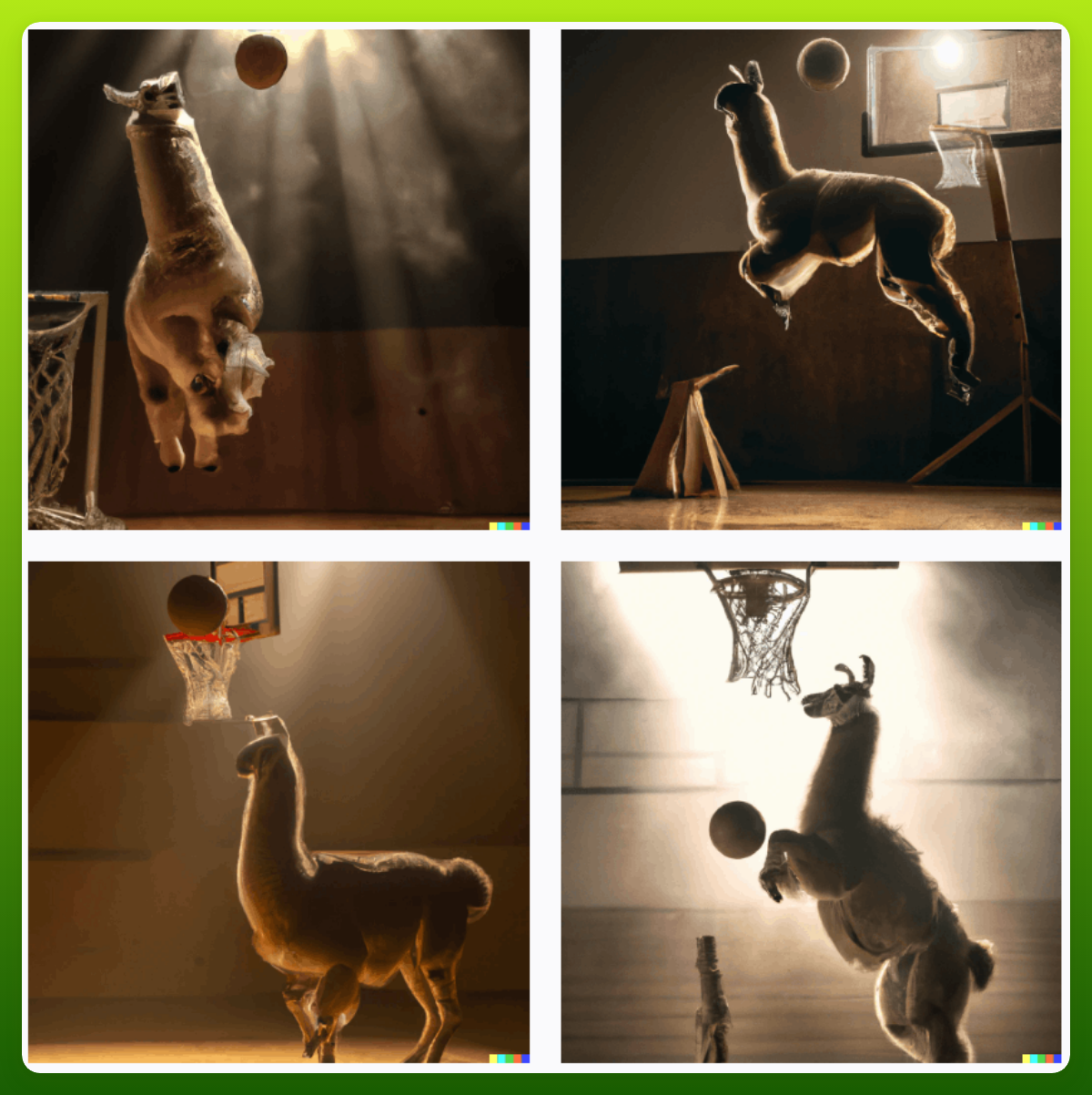

“film still of a llama wearing a jersey, dunking a basketball, low angle, long shot, indoors, dramatic backlighting, high detail.”

“film still of a llama in a jersey dunking a basketball like Michael Jordan, low angle, show from below, tilted frame, 35°, Dutch angle, extreme long shot, high detail, indoors, dramatic backlighting.”.

And just to show off how far we’ve come since September 2022, here’s what MidJourney AI did with the exact same prompt.
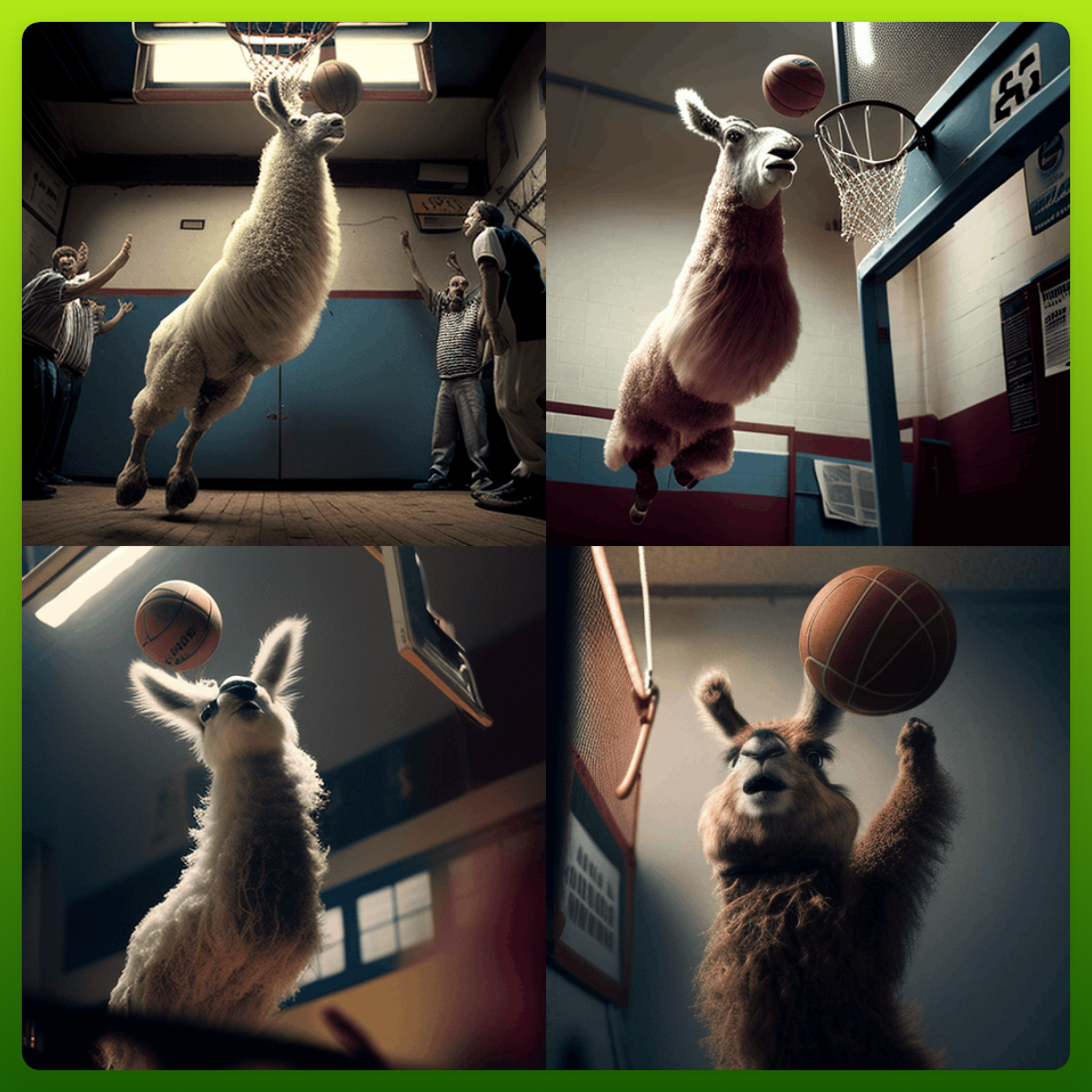

Looks like we’ve still got a ways to go.
Industrial Design
There’s so much more to “design” than just images. The design and development of mechanical and industrial components are being transformed by the use of AI at even the highest levels.
NASA is revolutionizing the process of designing mission hardware for space exploration with the use of AI. According to engineer Ryan McClelland, AI algorithms can generate thousands of potential designs and identify the best ones, resulting in hardware that is up to two-thirds lighter and three times stronger. The AI design process is also 10 times faster, taking as little as a week, compared to the traditional process of human designers taking weeks or even months to come up with a single design iteration.
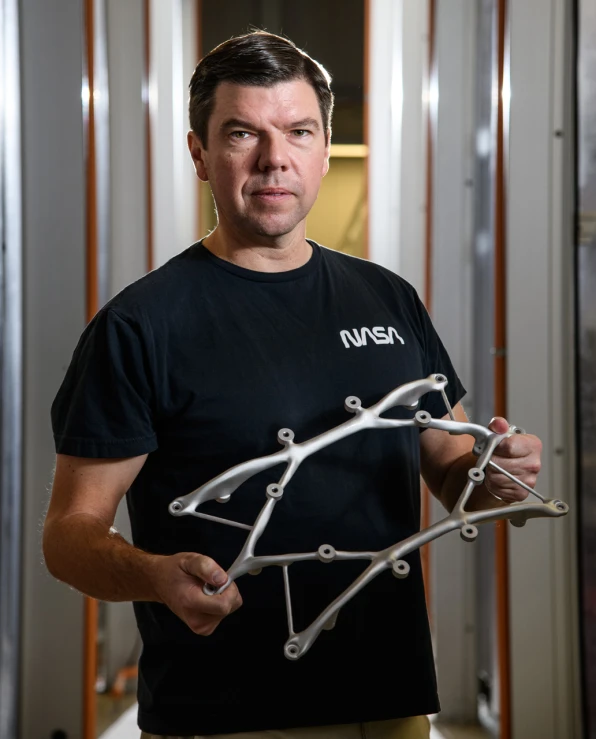

The system has been used to design a range of mission hardware, from scaffolds for NASA's balloon-borne EXCITE telescope to an optical bench for an ultraviolet imaging spectrometer. Designers can work alongside AI algorithms to refine designs and ensure they meet the requirements of the mission.
McClelland highlighted that the optical bench is one of the most impressive designs created by the AI system, as it has better structural performance and consolidated what would have been around 10 parts into a single part that can still be CNC machined.
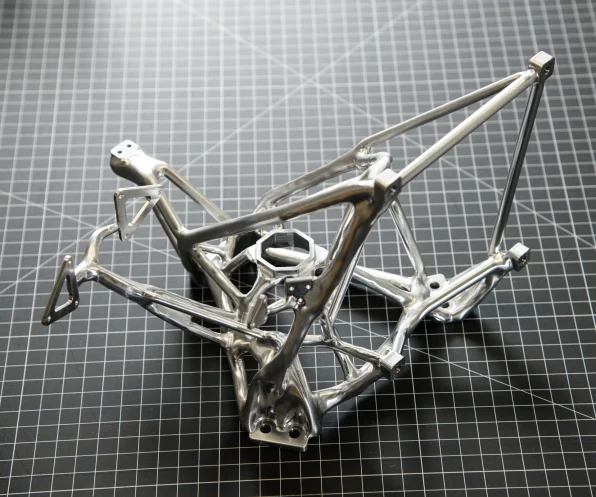

The AI design process for mission hardware involves several steps. Firstly, NASA identifies the mission requirements, which include specific goals and constraints. Then, AI algorithms generate thousands of potential designs based on the mission requirements. These designs are evaluated based on various criteria, including safety, efficiency, and cost. AI algorithms then identify the best designs based on the evaluation criteria.
Designers work alongside AI to refine the designs and ensure they meet the needs of the mission. The designers can modify the designs based on their expertise and feedback from the AI and the final designs are tested extensively to ensure they are safe, reliable, and efficient. The AI can identify potential problems in the designs that may have been missed by human designers. Finally, the designs are used to create the mission hardware, which is used in space exploration.
While today, the AI used at NASA is proprietary, it’s only a matter of time before it—or something like it—makes its way into the private sector.
German company Hyperganic has created a 3D-printed rocket engine that was completely designed by AI. The engine is unlike others as it is made up of only one single continuous piece, which has been designed to have the lowest weight and most effective cooling, resulting in the highest possible performance for a given rocket.
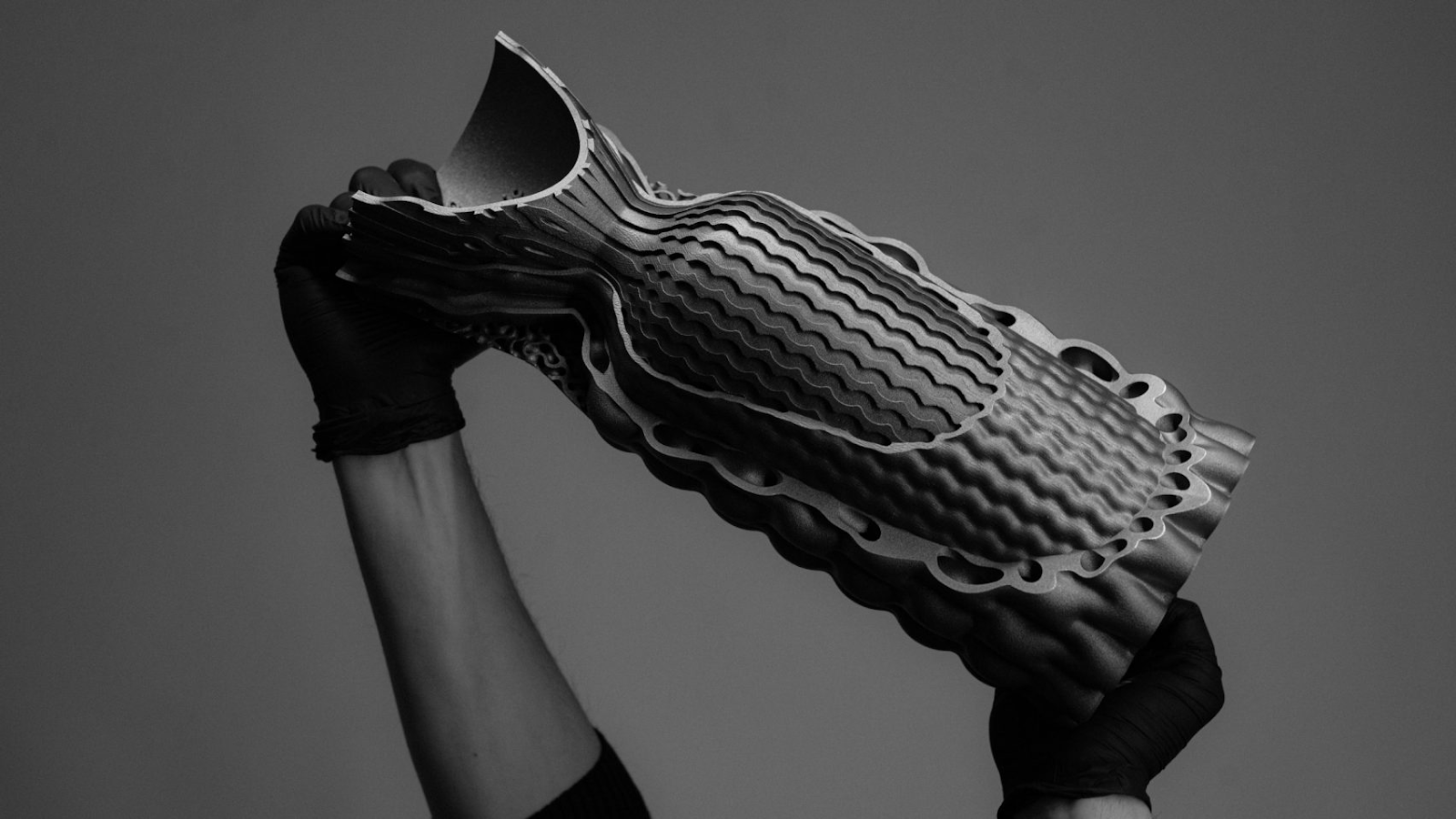

To create the engine, a rocket scientist first stipulated the core features of a rocket engine, such as the shape of the combustion chamber and the necessary cooling performance. This information was expressed as formulas and stored in an Excel sheet, in a format that could be read by Hyperganic's algorithm. The algorithm used the data to generate the geometry of the final piece from the bottom up.
The algorithm is self-optimizing, rendering one solution after another, always comparing. The new models are always generated from scratch. Every time you change your requirements, you get another rocket that is perfectly designed for the needs that you've set out.
The 3D-printed rocket engine demonstrates the potential for AI to revolutionize the design and manufacturing of complex components, and not just in the aerospace industry. The technology could be used in a range of industries to optimize the design of everything from engines to buildings, cars, and consumer products.
The benefits of using AI in the design process include the ability to generate thousands of potential designs quickly, identify the best ones, and refine the designs based on feedback from human designers. This results in optimal designs that are more efficient, cost-effective, and better suited to the needs of the application.
Hyperganic's 3D-printed rocket engine is an exciting example of how AI can be used to revolutionize the design and manufacturing of complex components. As technology continues to develop, we can expect to see more companies using AI to optimize their products and processes, resulting in better products that are more efficient, cost-effective, and better suited to the needs of their customers.
Further Reading
How to use AI to generate art.